Java ResultSet案例講解
ResultSet
ResultSet是我們使用jdbc連接時(shí),查詢的一個(gè)返回結(jié)果集,ResultSet resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(sql),下面就使用例子介紹ResultSet的使用
例子是通過(guò)jdbc連接查account表中的數(shù)據(jù),然后用實(shí)體類Account封裝起來(lái),返回這個(gè)類的集合。
jdbc工具類代碼
package com.lingaolu.Utils; import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.URL;import java.sql.*;import java.util.Properties; /** * @author 林高祿 * @create 2020-06-23-11:12 */public class JdbcUtils { private static String driver; private static String url; private static String userName; private static String pw; static{try { Properties p = new Properties(); ClassLoader classLoader = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader(); // 這個(gè)路徑相對(duì)于src的路徑來(lái)說(shuō) URL resource = classLoader.getResource('com/lingaolu/file/jdbc.properties'); String path = resource.getPath(); p.load(new FileReader(path)); driver = p.getProperty('driver'); url = p.getProperty('url'); userName = p.getProperty('user'); pw = p.getProperty('password'); Class.forName(driver);} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace();} } public static Connection createConnection() throws SQLException {return DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, pw); } public static void close(Statement stmt,Connection con){if(null != stmt){ try {stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }}if(null != con){ try {con.close(); } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }} } public static void close(ResultSet set,Statement s,Connection con){if(null != set){ try {set.close(); } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }}close(s,con); }}
Account實(shí)體類代碼
package com.lingaolu.jdbcConnector; /** * @author 林高祿 * @create 2020-06-24-8:28 */public class Account { private int id; private String name; private double balance; private int myAge; public int getId() {return id; } public void setId(int id) {this.id = id; } public String getName() {return name; } public void setName(String name) {this.name = name; } public double getBalance() {return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) {this.balance = balance; } public int getMyAge() {return myAge; } public void setMyAge(int myAge) {this.myAge = myAge; } @Override public String toString() {return 'Account{' +'id=' + id +', name=’' + name + ’’’ +', balance=' + balance +', myAge=' + myAge +’}’; }}
測(cè)試Demo3的代碼
package com.lingaolu.jdbcConnector; import com.lingaolu.Utils.JdbcUtils; import java.sql.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List; /** * @author 林高祿 * @create 2020-06-23-17:27 */public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) {String sql = 'select * from account';List<Account> accounts = fineAccount(sql);accounts.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println('----------------------------------');sql = 'select * from account where name=’張三’';accounts = fineAccount(sql);accounts.forEach(System.out::println); } public static List<Account> fineAccount(String sql){Connection con = null;Statement stmt = null;ResultSet resultSet = null;List<Account> rerurnList = new ArrayList<>();try { con = JdbcUtils.createConnection(); stmt = con.createStatement(); resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(sql); Account acc = null; while(resultSet.next()){// 引號(hào)里的字段要與表里的一樣int id = resultSet.getInt('id');String name = resultSet.getString('name');double balance = resultSet.getDouble('balance');int age = resultSet.getInt('age'); acc = new Account();acc.setId(id);acc.setName(name);acc.setBalance(balance);acc.setMyAge(age); rerurnList.add(acc); }} catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace();}finally { JdbcUtils.close(resultSet,stmt,con);}return rerurnList; }}
表中的數(shù)據(jù)
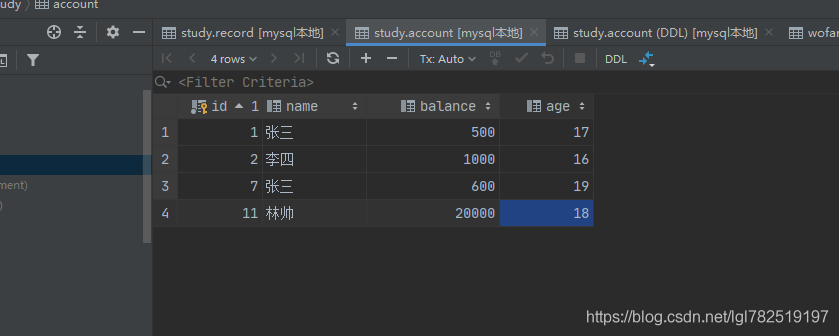
運(yùn)行輸出:
Account{id=1, name=’張三’, balance=500.0, myAge=17}Account{id=2, name=’李四’, balance=1000.0, myAge=16}Account{id=7, name=’張三’, balance=600.0, myAge=19}Account{id=11, name=’林帥’, balance=20000.0, myAge=18}----------------------------------Account{id=1, name=’張三’, balance=500.0, myAge=17}Account{id=7, name=’張三’, balance=600.0, myAge=19}
結(jié)果與預(yù)期的一致
到此這篇關(guān)于Java ResultSet案例講解的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Java ResultSet講解內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. Java類加載機(jī)制實(shí)現(xiàn)步驟解析2. XML入門的常見問(wèn)題(二)3. jsp文件下載功能實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼4. JSP之表單提交get和post的區(qū)別詳解及實(shí)例5. ASP中if語(yǔ)句、select 、while循環(huán)的使用方法6. IE6/IE7/IE8/IE9中tbody的innerHTML不能賦值的完美解決方案7. XML入門的常見問(wèn)題(一)8. ASP常用日期格式化函數(shù) FormatDate()9. ASP.NET MVC使用異步Action的方法10. ASP動(dòng)態(tài)網(wǎng)頁(yè)制作技術(shù)經(jīng)驗(yàn)分享
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備