使用Hangfire+.NET 6實現(xiàn)定時任務(wù)管理(推薦)
目錄
- 引入Nuget包和配置
- 編寫Job
- Fire and Forget
- Continuous Job
- Scehdule Job
- Recurring Job
- Run
- 長時間運行任務(wù)的并發(fā)控制???
- Job Filter記錄Job的全部事件
- 參考文章
在.NET開發(fā)生態(tài)中,我們以前開發(fā)定時任務(wù)都是用的Quartz.NET完成的。在這篇文章里,記錄一下另一個很強(qiáng)大的定時任務(wù)框架的使用方法:Hangfire。兩個框架各自都有特色和優(yōu)勢,可以根據(jù)參考文章里張隊的那篇文章對兩個框架的對比來進(jìn)行選擇。
引入Nuget包和配置
引入Hangfire相關(guān)的Nuget包:
Hangfire.AspNetCoreHangfire.MemoryStorageHangfire.Dashboard.Basic.Authentication
并對Hangfire進(jìn)行服務(wù)配置:
builder.Services.AddHangfire(c =>{ // 使用內(nèi)存數(shù)據(jù)庫演示,在實際使用中,會配置對應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)庫連接,要保證該數(shù)據(jù)庫要存在 c.UseMemoryStorage();});// Hangfire全局配置GlobalConfiguration.Configuration .UseColouredConsoleLogProvider() .UseSerilogLogProvider() .UseMemoryStorage() .WithJobExpirationTimeout(TimeSpan.FromDays(7));// Hangfire服務(wù)器配置builder.Services.AddHangfireServer(options =>{ options.HeartbeatInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10);});使用Hangfire中間件:
// 添加Hangfire Dashboardapp.UseHangfireDashboard();app.UseAuthorization();app.MapControllers();// 配置Hangfire Dashboard路徑和權(quán)限控制app.MapHangfireDashboard("/hangfire", new DashboardOptions{ AppPath = null, DashboardTitle = "Hangfire Dashboard Test", Authorization = new [] {new HangfireCustomBasicAuthenticationFilter{ User = app.Configuration.GetSection("HangfireCredentials:UserName").Value, Pass = app.Configuration.GetSection("HangfireCredentials:Password").Value} }});對應(yīng)的配置如下:
appsettings.json
"HangfireCredentials": { "UserName": "admin", "Password": "admin@123"}編寫Job
Hangfire免費版本支持以下類型的定時任務(wù):
- 周期性定時任務(wù):
Recurring Job - 執(zhí)行單次任務(wù):
Fire and Forget - 連續(xù)順序執(zhí)行任務(wù):
Continouus Job - 定時單次任務(wù):
Schedule Job
Fire and Forget
這種類型的任務(wù)一般是在應(yīng)用程序啟動的時候執(zhí)行一次結(jié)束后不再重復(fù)執(zhí)行,最簡單的配置方法是這樣的:
using Hangfire;BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Hello world from Hangfire with Fire and Forget job!"));Continuous Job
這種類型的任務(wù)一般是進(jìn)行順序型的任務(wù)執(zhí)行調(diào)度,比如先完成任務(wù)A,結(jié)束后執(zhí)行任務(wù)B:
var jobId = BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Hello world from Hangfire with Fire and Forget job!"));// Continuous Job, 通過指定上一個任務(wù)的Id來跟在上一個任務(wù)后執(zhí)行BackgroundJob.ContinueJobWith(jobId, () => Console.WriteLine("Hello world from Hangfire using continuous job!"));Scehdule Job
這種類型的任務(wù)是用于在未來某個特定的時間點被激活運行的任務(wù),也被叫做Delayed Job:
var jobId = BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Hello world from Hangfire with Fire and Forget job!"));// Continuous Job, 通過指定上一個任務(wù)的Id來跟在上一個任務(wù)后執(zhí)行BackgroundJob.ContinueJobWith(jobId, () => Console.WriteLine("Hello world from Hangfire using continuous job!"));Recurring Job
這種類型的任務(wù)應(yīng)該是我們最常使用的類型,使用Cron表達(dá)式來設(shè)定一個執(zhí)行周期時間,每到設(shè)定時間就被激活執(zhí)行一次。對于這種相對常見的場景,我們可以演示一下使用單獨的類來封裝任務(wù)邏輯:
IJob.cs
namespace HelloHangfire;public interface IJob{ public Task<bool> RunJob();}Job.cs
using Serilog;namespace HelloHangfire;public class Job : IJob{ public async Task<bool> RunJob() {Log.Information($"start time: {DateTime.Now}");// 模擬任務(wù)執(zhí)行await Task.Delay(1000);Log.Information("Hello world from Hangfire in Recurring mode!");Log.Information($"stop time: {DateTime.Now}");return true; }}在Program.cs中使用Cron來注冊任務(wù):
builder.Services.AddTransient<IJob, Job>();// ...var app = builder.Build();// ...var JobService = app.Services.GetRequiredService<IJob>();// Recurring jobRecurringJob.AddOrUpdate("Run every minute", () => JobService.RunJob(), "* * * * *");Run
控制臺輸出:
info: Hangfire.BackgroundJobServer[0]
Starting Hangfire Server using job storage: 'Hangfire.MemoryStorage.MemoryStorage'
info: Hangfire.BackgroundJobServer[0]
Using the following options for Hangfire Server:
Worker count: 20
Listening queues: 'default'
Shutdown timeout: 00:00:15
Schedule polling interval: 00:00:15
info: Hangfire.Server.BackgroundServerProcess[0]
Server b8d0de54-caee-4c5e-86f5-e79a47fad51f successfully announced in 11.1236 ms
info: Hangfire.Server.BackgroundServerProcess[0]
Server b8d0de54-caee-4c5e-86f5-e79a47fad51f is starting the registered dispatchers: ServerWatchdog, ServerJobCancellationWatcher, ExpirationManager, CountersAggregator, Worker, DelayedJobScheduler, RecurringJobScheduler...
info: Hangfire.Server.BackgroundServerProcess[0]
Server b8d0de54-caee-4c5e-86f5-e79a47fad51f all the dispatchers started
Hello world from Hangfire with Fire and Forget job!
Hello world from Hangfire using continuous job!
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: https://localhost:7295
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: http://localhost:5121
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Application started. Press Ctrl+C to shut down.
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Hosting environment: Development
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Content root path: /Users/yu.li1/Projects/asinta/Net6Demo/HelloHangfire/HelloHangfire/
[16:56:14 INF] start time: 02/25/2022 16:56:14
[16:57:14 INF] start time: 02/25/2022 16:57:14
[16:57:34 INF] Hello world from Hangfire in Recurring mode!
[16:57:34 INF] stop time: 02/25/2022 16:57:34
通過配置的dashboard來查看所有的job運行的狀況:
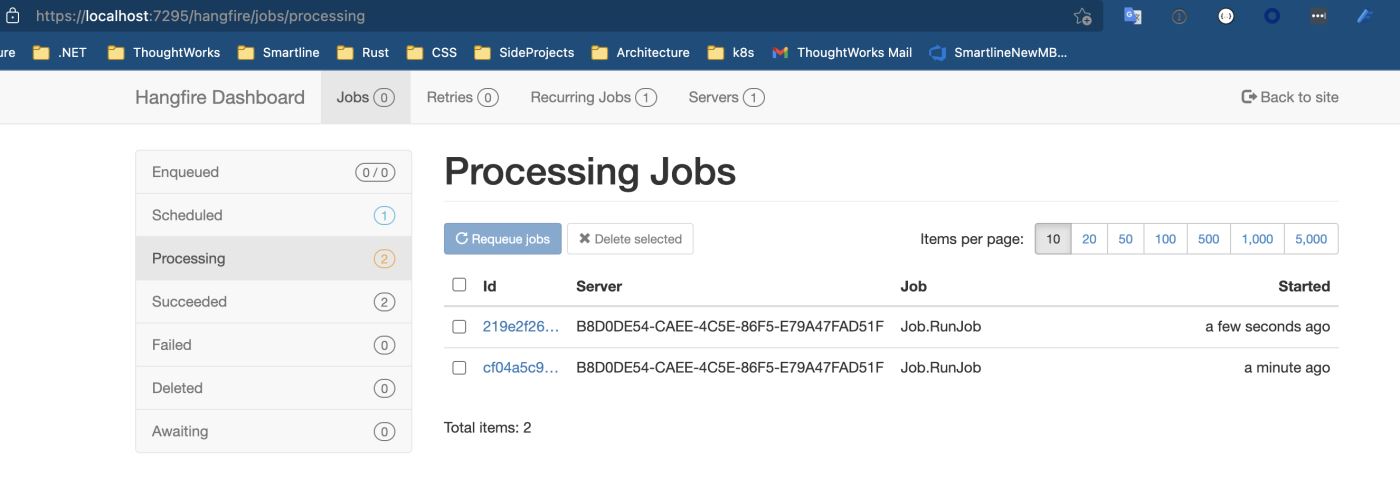
長時間運行任務(wù)的并發(fā)控制???
從上面的控制臺日志可以看出來,使用Hangfire進(jìn)行周期性任務(wù)觸發(fā)的時候,如果執(zhí)行時間大于執(zhí)行的間隔周期,會產(chǎn)生任務(wù)的并發(fā)。如果我們不希望任務(wù)并發(fā),可以在配置并發(fā)數(shù)量的時候配置成1,或者在任務(wù)內(nèi)部去判斷當(dāng)前是否有相同的任務(wù)正在執(zhí)行,如果有則停止繼續(xù)執(zhí)行。但是這樣也無法避免由于執(zhí)行時間過長導(dǎo)致的周期間隔不起作用的問題,比如我們希望不管在任務(wù)執(zhí)行多久的情況下,前后兩次激活都有一個固定的間隔時間,這樣的實現(xiàn)方法我還沒有試出來。有知道怎么做的小伙伴麻煩說一下經(jīng)驗。
Job Filter記錄Job的全部事件
有的時候我們希望記錄Job運行生命周期內(nèi)的所有事件,可以參考官方文檔:Using job filters來實現(xiàn)該需求。
參考文章
關(guān)于Hangfire更加詳細(xì)和生產(chǎn)環(huán)境的使用,張隊寫過一篇文章:Hangfire項目實踐分享。
到此這篇關(guān)于使用Hangfire+.NET 6實現(xiàn)定時任務(wù)管理的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān).NET 定時任務(wù)管理內(nèi)容請搜索以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持!
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備